Research
The MIT Game Lab has a long history of innovative research that spans game culture to design practice. Below are some highlights of our work. See specific pages in the pull down menu for more detailed information on some of them.
Games & Colonialism
2017-: Mikael Jakobsson (co-PI), Mary Flanagan (co-PI)
What does the history of colonialism-themed board games look like, and what can it tell us about the situation today? What does it mean to present these historical moments in such a lavish form and then let these artifacts serve as centerpieces to gather around for social interaction at board game cafes, meetups, and conventions? This greater project includes Playing Oppression, a forthcoming book to be published by MIT Press; Orderly Adventures, in which we play and analyze games with colonialist themes; and Creating Counter-Colonial Games, a series of workshops to prototype games through cultural engagement with people affected by the colonialist endeavor.
Diversity and Inclusion in Esports and Gaming
2015-: T.L. Taylor
Launched in 2015, AnyKey was co-founded by Dr. T.L. Taylor and Dr. Morgan Romine (with support from Intel and ESL) with the goal of building a more inclusive and accessible esports world for all. Since that inception, AnyKey has become the leading advocacy organization for inclusion and diversity in competitive gaming & live streaming. It now operates as a non-profit and Dr. Taylor has transitioned from being the Director of Research to Chair of the Advisory Board.
Playful Augmented Reality Audio Design Exploration
2018-2019: Mikael Jakobsson & Philip Tan
The focus of this project was to explore the potential of audio augmented reality (AR) technology through design research methodology, particularly exploratory prototyping. Going into this, we understood that location-based audio AR allows the potential for telling stories using the players lived world, through innovative use of the affordances of mobile phone devices, particularly GPS. We also considered audio AR as a means of playing with sound and music. Utilizing the accelerometers of the Bose AR glasses and connected mobile device, body movement can be linked to the players’ own music collection or a music generation engine.
Our work culminated in the discovery of what we are calling locomotion-based gameplay, a modification to the assumptions that occur when considering location- based gameplay. From our explorative work, locomotion-based gameplay arises from the affordances and limitations of current audio AR technology. It considers a person’s movement through space as important, more so than their precise location. Locomotion also implies whole body movement through gestures including the nod of a head and the tap of a toe, not just the vector of movement on a map. These gestures are ephemeral and contain multiple meanings dependent on context and mood. We believe more work in discovering this style of gameplay would be fruitful, for purposes of art and entertainment, for education and tourism, and other currently unforeseen use cases.
Intimate Worlds: Reading for Intimate Affects in Contemporary Video Games
2016-2018: Kaelan Doyle-Myerscough (S.M., Comparative Media Studies, 2018)
When we think of pleasures to be found in video games, we often talk about power, control, agency, and fun. But to center these pleasures is to privilege certain stories, players, actions and possibility spaces. This thesis uses the framework of intimacy to closely examine three games for their capacity to create pleasure in vulnerability, the loss of control, dependence on others, and precarity.
Drawing from Deleuzian affect theory and feminist, queer and posthuman theorists, I read for intimate affects in the formal, aesthetic, proprioceptive and structural elements of Overwatch, The Last Guardian and The Legend of Zelda: Breath of the Wild. Ultimately, I argue two points: that video games have a unique capacity to generate intimate affects, and that my games of choice push us to rethink our assumptions about what constitutes intimacy more broadly.
When All You Have is a Banhammer: The Social and Communicative Work of Volunteer Moderators
2016-2018: Claudia Lo (S.M., Comparative Media Studies, 2018)
The popular understanding of moderation online is that moderation is inherently reactive, where moderators see and then react to content generated by users, typically by removing it; in order to understand the work already being performed by moderators, we need to expand our understanding of what that work entails. Drawing upon interviews, participant observation, and my own experiences as a volunteer community moderator on Reddit, I propose that a significant portion of work performed by volunteer moderators is social and communicative in nature. Even the chosen case studies of large-scale esports events on Twitch, where the most visible and intense tasks given to volunteer moderators consists of reacting and removing user-generated chat messages, exposes faults in the reactive model of moderation. A better appreciation of the full scope of moderation work will be vital in guiding future research, design, and development efforts in this field.
Recasting Player Two
2016-2017: Mikael Jakobsson, Claudia Lo, Kaelan Doyle Myerscough, Richard Eberhardt & Dozens of Game Designers From Near and Far

The game development industry is currently on a mission to include “non-gamers” in local co-op games. Within the development community and among players, these games are said to have a “girlfriend mode.” Developers often cast player one as an expert player in their own image, while player two is a projection of antiquated gender stereotypes who has less agency and control over their play experience. This type of interaction would be better described as mansplaining in motion. This project consists of a series of workshops with participants from the game development community, where we not just discuss and spread awareness of what is problematic with current games and development practices, but work together in creating better alternatives.
OpenRelativity
2012-2016: Gerd Kortemeyer, Philip Tan, Zach Sherin, Ryan Cheu, & Steven Schirra
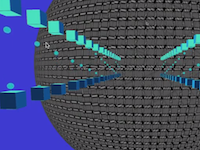
OpenRelativity is an open-source toolkit to simulate effects of special relativity by varying the speed of light, developed to help people create, test, and share experiments to explore the effects of special relativity. Developed by the MIT Game Lab, it contains open-source code for public use with the free and paid versions of the Unity engine. The toolkit was developed during the creation of the game A Slower Speed of Light.
Gender and Systems of Warm Interaction in Digital Games
2014-2016: Kyrie Caldwell (S.M., Comparative Media Studies, 2016)

This thesis considers the ways in which digital game mechanics (interactive inputs) contribute to games’ worldbuilding. In particular, this work is concerned with the replication and reinforcement of problematic gender roles through game mechanics that express positive (“warm”) interactions between characters, namely healing, protection, and building relationships. Characters who are women and girls are often associated with physical weakness, nature-based magic, and nurturing (or absent) personalities, whereas characters who are men and boys often protect women through physical combat, heal through medical means, and keep an emotional distance from others. Relationships built through game mechanics rely on one-sided agency and potential that renders lovers and friends as characters who exist to support the player character in achieving the primary goals of the game. Even warm interactions in games carry negative, even potentially violent and oppressive, representations and that there is thusly a need for design interventions on the mechanical level to mitigate violence in game worlds and the reinforcement of negative real world stereotypes.
E-sports Broadcasting
2014-2015: Jesse Sell (S.M., Comparative Media Studies, 2015)
Situating e-sports broadcasting within the larger sports media industrial complex, discussing e-sportscasters, and investigating the economics behind the growing e-sports industry. E-sports, often referred to as competitive or professional gaming, stands as a prime example of the merger of work and play. A growing body of literature has started focusing on this pastime turned profession. As more professionals enter the scene and audiences continue to grow, e-sports broadcasters look towards older models of broadcasting to inform their own style. This reapplication of former conventions stands in contrast to the trends in the larger sports media trajectory. E-sports broadcasting is largely informed by traditional sports broadcasting, yet remains unable to fully capture the success of the global sports industry. On-air talent, once informed solely by traditional sportscasters are now looking to their fellow e-sportscasters to create something new. Revenue streams which form the foundation of the sports industry are making their way into e-sports but not in the way that one might expect.
MIT Overseer: Improving Observer Experience in Starcraft 2
2013-2015: Philip Tan & Nick Mohr

The MIT Overseer project aims to provide casters with real-time graphics to help them tell the story of a game while it is in progress. We are trying out several different ways of displaying what happened in the past of a single game and anticipating what might happen in the near future.
Subversive Game Design and Meaningful Conflict
2012-2013: Konstantin Mitgutsch & Steven Schirra

Movers & Shakers is used as a research tool to explore how a social component influences experiences in serious games. In addition subversive game design elements are implemented in the game to foster the players’ thinking process and to get them out of unquestioned routines. In the game the players are challenged to give up their prior egoistic goals to reach their common goal – to save the world. In a nutshell, the game shifts from a competitive to a collaborational gameplay – once the players start communicating.
Playstyle Motivation Explorations
2012-2013: Todd Harper
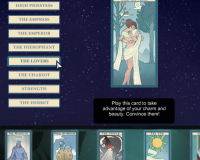
Across game genres and communities, there are as many styles of play as there are players, from the highly competitive “powergamer” to the MMO fan who’s content to just take in the scenery and everything in between. Fugue is a game that asks: what are some of the motivations behind these styles? Do players reflect themselves — or a desired projection of the self — through playstyle? Or does the shape and context of the game itself direct such decisions? In order to explore these questions, we created a small, controlled gamespace that gives players an opportunity to express themselves via play.
Procedural Puzzles as a Design Tool for Games
2011-2013: Alec Thomson, Clara Fernández-Vara
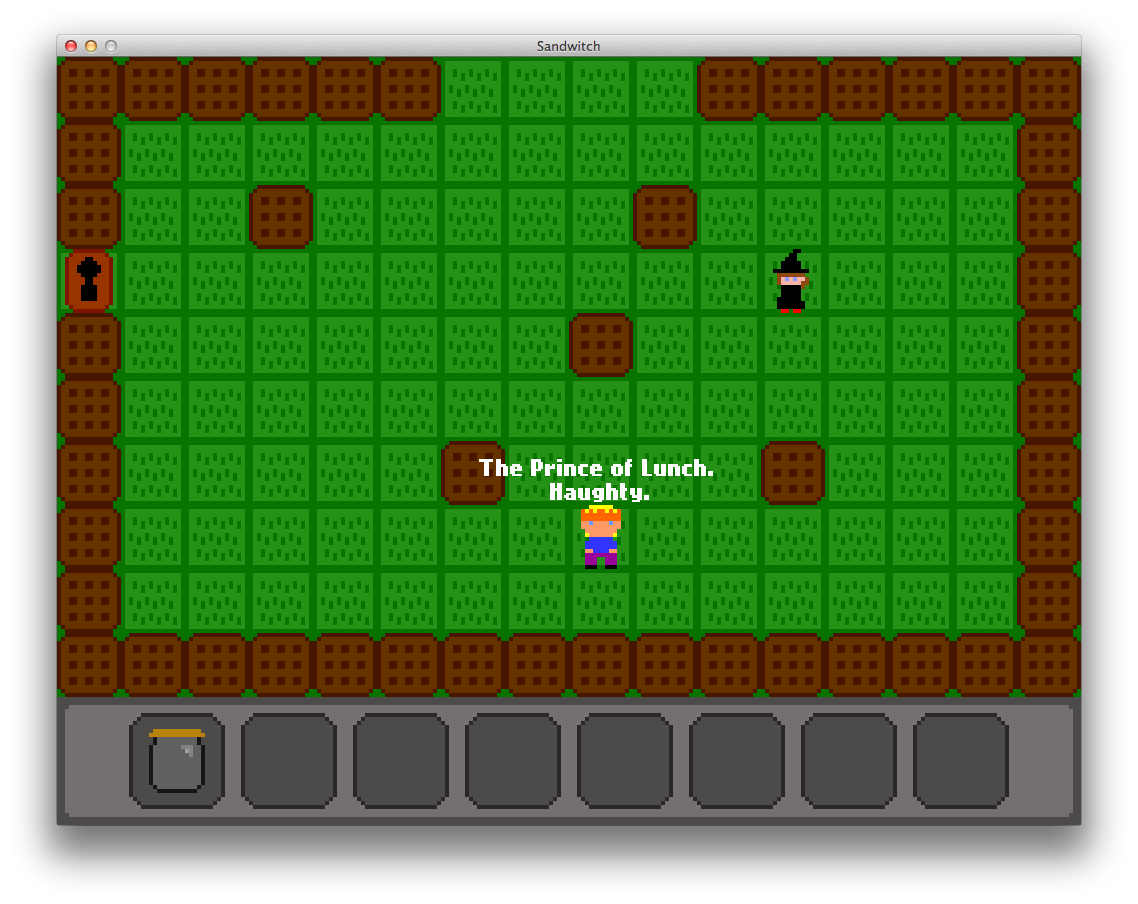
Puzzledice is a set of tools and programming libraries for procedurally generating puzzles for a wide variety of games. These tools, developed by Alec Thomson at the MIT Game Lab from 2011-2013, are the result of multiple iterations of research and were used to develop Stranded in Singapore during the 2011 summer session of the Singapore-MIT GAMBIT Game Lab. Puzzledice is the result of research into how general purpose procedural puzzles can be used as a tool by game designers. These tools were designed to meet the following three goals: Solvability, Generality, and Usability.
Televisual Sports Videogames
2012-2013: Abe Stein (S.M., Comparative Media Studies, 2013)

Over the three decade long history of sports videogame development, design conventions have lead to the emergence of a new sports game genre: the televisual sports videogames. These games, which usually simulate major professional or college sports, look and sound like television, and they use televised sports as a reference point for players. This thesis takes a critical look at how these televisual sports videogames are situated in the broader sports media industrial complex of North America, while also considering how the televisual design of these games is meaningful for fans of sports. Specifically, the text looks at how sports videogames reflect or reinforce dominant ideologies of hegemonic sports culture. Building on critical theories in sports studies, and through critical close readings of videogame texts, this thesis explores the relationship between sports television production, and sports videogames, with a focus on features that are found in both. Features such as introductory sequences, audio commentary, in-game advertising, news tickers, and instant replay are all commonly found in both sports television and sports videogames.
Purposeful Games for Social Change
2011-2012: Konstantin Mitgutsch & Narda Alvarado

“Purposeful Games for Social Change” is a list of serious games designed to foster social change/justice or to raise awareness. This list was created in order to create the Purposeful Games Framework, a tool used to assess the cohesiveness in design of serious games.
Singapore-MIT GAMBIT Game Lab
2007-2012

The Singapore-MIT GAMBIT Game Lab was a six-year research initiative that addressed important challenges faced by the global digital game research community and industry, with a core focus on identifying and solving research problems using a multi-disciplinary approach that can be applied by Singapore’s digital game industry. The Singapore-MIT GAMBIT Game Lab focused on building collaborations between Singapore institutions of higher learning and several MIT departments to accomplish both research and development.
Research topics explored included artificial intelligence, game design, computer graphics and animation, character design, procedurally generated content, interactive fiction, narrative design, and video game production. Game prototypes were made for these research topics during the GAMBIT summer internship program, many of which won international recognition at festivals like IndieCade and the Independent Games Festivals held at GDC and GDC China, as well as academic conferences such as Meaningful Play and Foundations of Digital Games.
